top of page
MOSTLY MICROBES AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Welcome to Mostly Microbes and Infectious Diseases. David Ojcius posts newspaper and journal articles in the broad field of microbiology.

Search


Boswellia serrata Extract and Its Bioactive Compound, 3-O-Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic Acid (AKBA), Induce ROS-Mediated Intracellular Clearance of Porphyromonas gingivalis in Gingival Epithelial Cells
Porphyromonas gingivalis is a keystone pathogen in periodontitis, known for its ability to invade gingival epithelial cells and persist intracellularly. Conventional antimicrobials are often ineffective against intracellular pathogens, and natural products remain poorly explored in this context. Here, we investigated the antimicrobial effects of Boswellia serrata extract and its bioactive compounds on the dynamics of P. gingivalis infection in human gingival epithelial
David Ojcius
23 hours ago1 min read


Cellular senescence as a therapeutic target for aging intervention
Highlights Senescent cells drive aging, chronic disease, and tissue dysfunction Senotherapeutics span senolytics, senomorphics, immunotherapy, and restoration Target selection, screening readouts, and delivery platforms are linked to senescent-state biology to improve selectivity and translation Abstract Cellular senescence is a stress-induced cellular state that contributes to tissue dysfunction, chronic inflammation, and a broad range of aging-associated pathologies. The ac
David Ojcius
2 days ago1 min read


Mitochondrial transfer from immune to tumor cells enables lymph node metastasis
Highlights Cancer cells hijack mitochondria from many immune cells Mitochondria loss by immune cells impairs innate and adaptive anti-tumor immunity Fusion of hijacked and endogenous cancer cell mitochondria triggers cGAS STING activation cGAS-STING activation promotes lymph node metastasis through type I interferon signaling Summary Although the immune system is a significant barrier to tumor growth and spread, established tumors evade immune attack and frequently colonize i
David Ojcius
2 days ago1 min read


TseVF-TsiVF, a novel bacteriolytic effector-immunity pair of Vibrio fluvialis VflT6SS2, provides a fitness advantage in microbial competition
Highlight T6SS effector TseVF demonstrates apparent bacterial killing activity in the periplasm. TseVF interacts with phosphate lipid molecules and compromises the integrity of the cell membrane. The C-terminal region of TseVF is responsible for its bactericidal activity. 4. TsiVF binds to and neutralizes TseVF toxicity. TseVF secretion and bactericidality requires the C terminus of a cognate VgrG protein (TssI2_b). Abstract Vibrio fluvialis ( V. fluvialis ) is a halophilic
David Ojcius
3 days ago2 min read


Diversity and Transmission Processes of Potentially Pathogenic Bacterial Communities in the East Rongbuk Glaciers, Mt. Everest
Highlights A total of 833 glacier-derived potential pathogens were identified across habitats. Altitude and TOC drive distinct patterns of pathogen diversity in glacier habitats. Moraine and cryoconite are key sources of downstream pathogen dispersal. Community assembly is mainly stochastic, with network structure shaping selection. Cryospheric biosafety risks emerge via airborne and meltwater transmission pathways. Abstract Glacier retreat driven by global warming is releasi
David Ojcius
3 days ago2 min read


Parabacteroides
Parabacteroides is a Gram-negative , anaerobic , non- spore -forming genus from the family Tannerellaceae . First isolated from fecal specimen in 1933, type strain Parabacteroides distasonis was originally classified under the name Bacteroides distasonis. The strain was re-classified to form the new genus Parabacteroides in 2006. Parabacteroides currently comprise 21 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species, 11 of which are listed in the t
David Ojcius
Jan 121 min read


Biocontrol efficiency of native Bacillus sp. HC-9 on honeysuckle leaf spot caused by Alternaria alternata
Highlights Bacillus sp. HC-9 controls honeysuckle leaf spot caused by A. alternata. Strain HC-9 inhibits eight phytopathogenic fungi with strong antifungal activity. Strain HC-9 induces ROS and activates defense enzymes in honeysuckle leaves. Field trials show HC-9 achieves up to 80.52% disease control efficiency. Abstract Honeysuckle leaf spot disease, caused by Alternaria alternata , severely affects the yield and quality of honeysuckle crops. Biological control using nati
David Ojcius
Jan 92 min read


The TamA protein as a subunit vaccine improves immune protection against highly virulent Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in mice
Highlights Identification of the TamA protein as a highly conserved antigen across diverse Klebsiella pneumoniae strains, making it an ideal target for a broad-spectrum subunit vaccine. Development and evaluation of a recombinant TamA protein vaccine that significantly enhances immune protection against a highly virulent Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a murine model. Demonstration of TamA-induced specific antibodies that effectively inhibit bacterial adherence to epithe
David Ojcius
Jan 92 min read


Chlamydiose
Chlamydiosen sind durch verschiedene Chlamydien (bestimmte Bakterienarten ) verursachte Infektionskrankheiten . Sie betreffen das Auge (als Trachom ), die Atemwege und die Lunge (als Pneumonie ) und den Urogenitaltrakt (Harn- und Geschlechtsorgane) als sexuell übertragene Krankheit . Von genitalen Chlamydien-Infektionen sind überwiegend Jugendliche und junge Erwachsene im Alter von 15 bis 24 Jahren betroffen. Urogenitale Chlamydien-Infektionen verlaufen häuf
David Ojcius
Jan 81 min read


Phospholipid Diversity and Biosynthesis Pathway in Bacteria: Potential Antibacterial Targets
Highlights Phospholipid diversity shapes membrane properties for growth and stress adaptation Bacteria remodel phospholipid head groups and acyl chains to resist antimicrobials Phospholipid and its metabolism serve as promising potential antibacterial targets Abstract Bacterial infections have posed a serious threat globally. The discovery of new targets and the development of novel antimicrobial agents are urgently needed to combat these bacterial infections. The bacterial m
David Ojcius
Jan 61 min read


Isolation, Identification, and Plant Growth-Promoting Mechanisms of Strain BN5, with a Focus on Exogenously Trp-Independent IAA Biosynthesis, and Its Impact on Cucumber Cultivation
Highlights First systematic report of Niallia taxi BN5 with plant growth-promoting (PGP) activity, filling the Niallia PGP mechanism gap (previously studied for bioremediation/antibacterial functions). Multi-omics (genome/transcriptome/qPCR) show BN5 has a complete trp operon for constitutive IAA biosynthesis (17.64 μg/mL); tryptophan regulates trp/motility genes. BN5 enhances cucumber growth (height +24.29%, stem +11.23%), yield (+17.55%) and quality (vitamin C +17.2%, sol
David Ojcius
Jan 62 min read


Vaccines Are Helping Older People More Than We Knew
Many shots seem to have “off-target” benefits, such as lowering the risk of dementia, studies have found. Let’s be clear. The primary reason to be vaccinated against shingles is that two shots provide 90 percent protection against a painful, blistering disease that a third of Americans will suffer in their lifetimes, one that can cause lingering nerve pain and other nasty long-term consequences. The most important reason for older adults to be vaccinated against the respirat
David Ojcius
Jan 61 min read


Differences in Gut Microbiota Composition Are an Important Reason for Lower Serum P-Cresol Sulfate Levels in anuric Peritoneal Dialysis Patients Compared to Hemodialysis Patients
Highlights Distinct microbial communities are found in peritoneal dialysis (PD) and paired hemodialysis (HD) patients, despite similar microbiome diversity. Serum p-cresyl sulfate (PCS) levels are significantly lower in PD patients compared to paired HD patients. Altered microbial composition in PD patients, featuring more opportunistic pathogens and fewer beneficial bacteria, is linked to differences in metabolite profiles. Fecal transplant experiments confirm that the HD-as
David Ojcius
Jan 52 min read


Microbial metabolism in deep terrestrial subsurface communities - amino acids as biosignatures
Highlights Salinity and nutrient availability affect the utilization and secretion of amino acids by deep biosphere microbial consortia Anoxic deep biosphere enrichment cultures were compared to Desulfovibrio desulfuricans Amino acids and organic acids were degraded under different nutrient conditions Phe and Val degradation remained unaffected by changes in nutrient availability Metabolic pathways involving Phe, Cys and Met were most prominent Abstract The deep terrestrial s
David Ojcius
Jan 31 min read


Vegetation composition shapes denitrifier community structure and enhances nitrogen removal in estuarine wetlands: evidence from Reed-Willow Mix promoting nirK-dominated guilds
Highlights Mixed reed and willow vegetation boosts denitrification more than monocultures. nirK denitrifiers are major drivers of N removal variation over nirS . Soil depth reshapes denitrifiers: nirS depth-sensitive, nirK nutrient-responsive. Reed-willow boosts network complexity with depth to foster microbial interactions. Bradyrhizobium, Sinorhizobiu m, and Mesorhizobium are key to mitigating N loss. Abstract Estuarine wetlands are critical biogeochemical hotspots
David Ojcius
Jan 32 min read


A longitudinal profiling of microbiome of diabetic foot ulcers shows functional role of microbial communities in wound worsening and chronicity
Highlights Pseudomonas, Escherichia and Prevotella dominated DFU assemblage across visits Alcaligenes dominated healed DFU while Enterococcus was abundant in worsened DFU High HbA1c favored Pseudomonas while Prevotella was abundant in lower HbA1c samples Amputated DFUs had increased abundance of Escherichia and reduced Staphylococcus Microbiome functional profiles in worsened DFU were enriched in virulence factors Abstract Microbial communities in infected diabetic foot ulcer
David Ojcius
Jan 12 min read


Butyrolactol A enhances caspofungin efficacy via flippase inhibition in drug-resistant fungi
Highlights Butyrolactol A synergizes with caspofungin against cryptococci and Candida auris BLA restores echinocandin efficacy by targeting the Apt1-Cdc50 flippase complex Cryo-EM shows BLA traps the Apt1-Cdc50 phospholipid flippase in a dead-end state BLA blocks lipid transport, disrupts membrane homeostasis, and boosts drug uptake Summary Fungal infections cause millions of deaths annually and are challenging to treat due to limited therapeutic options and rising resistance
David Ojcius
Jan 11 min read


A look into the virosphere of clouds: a world yet to be explored
Highlights Viruses are largely overlooked in outdoor aeromicrobiological studies Based on current knowledge in aeromicrobiology, a total of 10 21 virus particles are estimated to occupy clouds globally Although very dilute, these may contribute to the atmospheric life cycle of microorganisms Virus-bacteria interactions in clouds would have many implications in ecology and the Earth’s microbiome Abstract Clouds are aqueous atmospheric systems hosting diverse and active microo
David Ojcius
Jan 11 min read

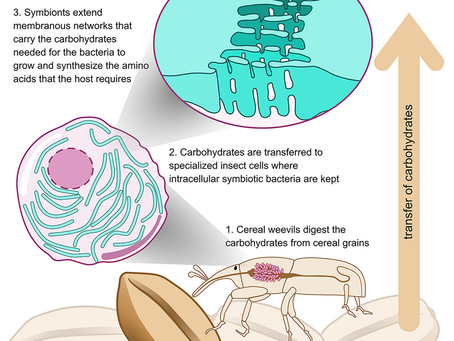
Bacterial tubular networks channel carbohydrates in insect endosymbiosis
Highlights • V olume electron microscopy unveils intensive membrane networks in insect symbiotic cells • These tubenets are formed by intracellular bacteria, the insect’s nutritional symbionts • In situ high spatial resolution chemical analysis shows tubenets’ enrichment in sugar • Bacterial tubenets increase the interface of exchange, maximizing nutrient acquisition Summary Symbiosis is widespread in nature and plays a fundamental role in organism adaptation and evolution.
David Ojcius
Dec 31, 20251 min read

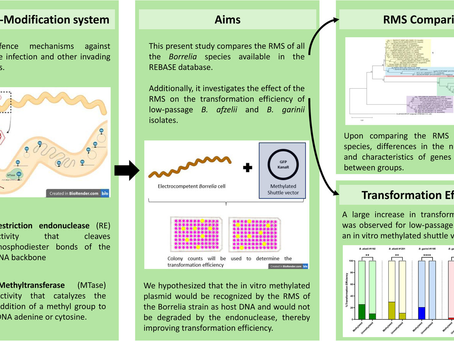
Comparative Analysis of Borrelia’s Defence Mechanisms and Their Impact on Genetic Manipulation of Low-Passage Isolates of Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii
Highlights The Borrelia restriction-modification system (RMS) differs by species group. The RMS affects the transformation efficiency of Borrelia. Increase in transformation efficiency observed with an in vitro methylated vector. Transformation efficiency increased in low-passage Borrelia strains. In vitro methylation can be a facilitating tool for Borrelia genetic manipulation. Abstract Borrelia, a highly prevalent tick-borne pathogen, has a genome with a linear chromoso
David Ojcius
Dec 28, 20252 min read
Home: Blog2
Home: Subscribe

Home: Contact
bottom of page













